Edge Computing: Bringing Processing Closer to Data
Why Is Edge Computing Suddenly Taking Center Stage?
Imagine a world where your self-driving car reacts to a pedestrian milliseconds before a collision, or a factory robot adjusts its movements in real-time based on sensor data. This isn’t science fiction,
it’s the rapidly evolving reality powered by Edge Computing.
For years, data processing relied heavily on centralized cloud servers.
But with the explosion of IoT devices, the increasing demand for real-time applications, and the need for enhanced data privacy, a new paradigm has emerged.
This blog post dives deep into Edge Computing, exploring its core principles, market trends, practical applications, and crucial considerations for businesses and technology enthusiasts alike.
Key Concepts & Trends
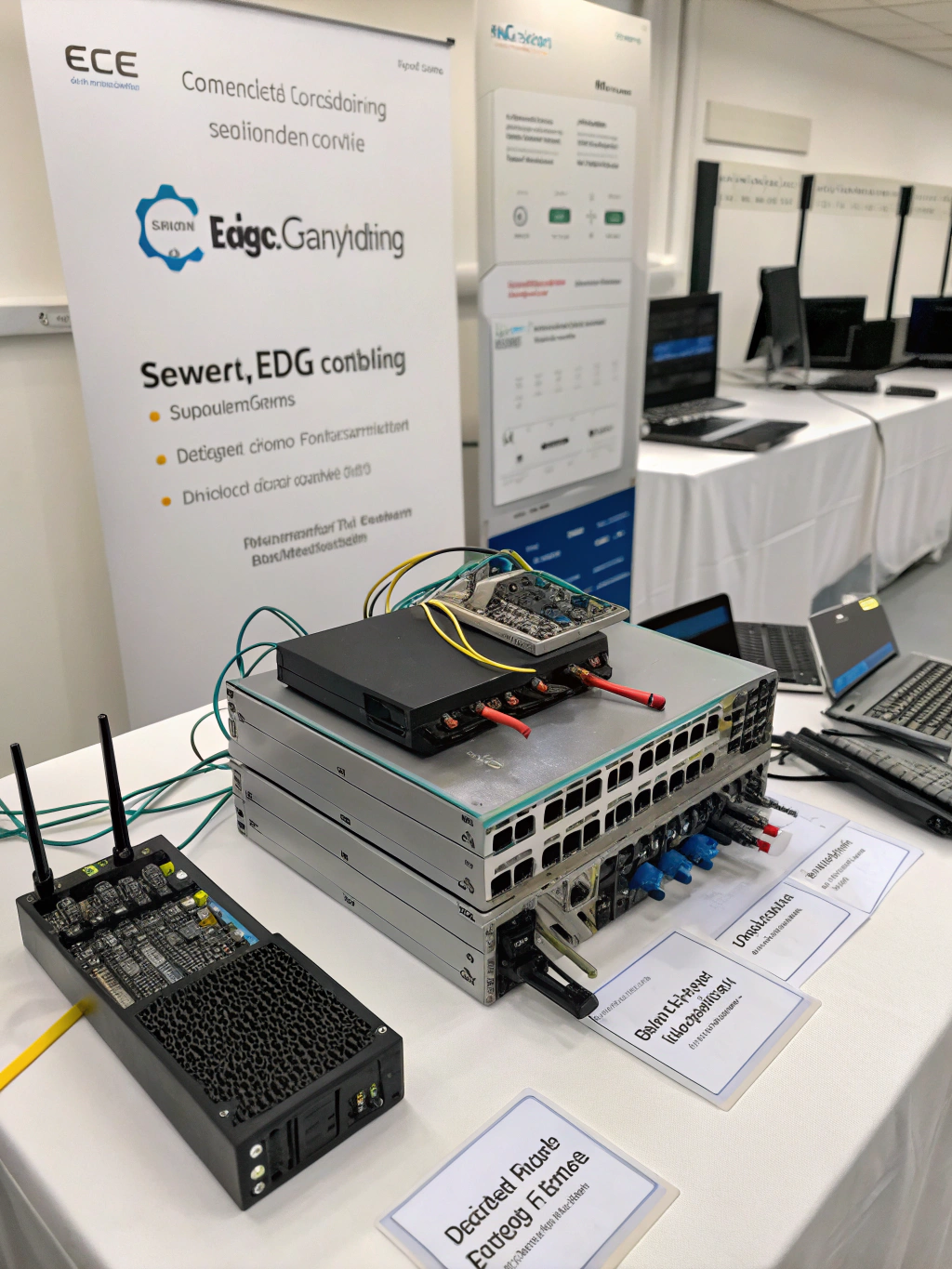

At its heart, Edge Computing is about bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data — be it devices, sensors, or endpoints. This contrasts with traditional cloud computing, where data is sent to a remote data center for processing. Several key trends are driving the adoption of this technology:
- Distributed Architecture: The move towards Decentralized Computing fuels the growth of edge networks. Instead of a single point of failure, processing power is distributed across multiple edge devices and locations. This enhances resilience and reduces latency.
- 5G and Enhanced Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks provides the high bandwidth and low latency required for seamless edge computing applications. Faster data transfer enables quicker decision-making at the edge.
- AI at the Edge: Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning models directly onto edge devices reduces the need to transmit large datasets to the cloud for analysis. This unlocks real-time insights and autonomous operations.
- Serverless Edge: This emerging trend allows developers to deploy and run applications on edge infrastructure without managing underlying servers, simplifying deployment and scaling.
- Microservices Architecture: Breaking down applications into smaller, independent services makes them more adaptable and easier to deploy across distributed edge environments.
Think of it like this: traditionally, all ingredients for a meal had to be shipped from a central warehouse (the cloud). With Edge Computing, some ingredients are stored in local pantries (edge devices) for quicker access and faster meal preparation.
Data & Market Insights
The Edge Computing market is experiencing explosive growth. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global edge computing market is projected to reach USD 67.76 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 35.2% from 2023. This surge is fueled by the proliferation of IoT devices across industries like manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and transportation.
Consider the automotive industry: autonomous vehicles rely on real-time data processing to navigate safely. Tesla, for instance, utilizes powerful onboard computers (an example of edge infrastructure) to make split-second decisions.
Another compelling statistic comes from a report by IDC, which highlights that over 70% of digital enterprises are considering or have already adopted edge computing initiatives. This indicates a significant shift in how businesses are approaching data processing and application deployment.
(Infographic: A bar chart showing the projected growth of the Edge Computing market from 2023 to 2028, incorporating data from MarketsandMarkets.)
Smarter Strategies & Alternatives
Optimizing your approach to Edge Computing involves careful consideration of your specific needs and resources. Here are a few strategies:
- Hybrid Cloud Approach: Don’t abandon the cloud entirely. A hybrid model leverages the strengths of both cloud and edge computing, using edge for real-time processing and the cloud for long-term storage and complex analytics.
- Containerization: Using technologies like Docker and Kubernetes simplifies the deployment and management of applications across diverse edge environments.
- Open Source Platforms: Platforms like Kubernetes and various edge-specific frameworks offer cost-effective and flexible solutions.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with experienced edge computing providers can accelerate deployment and reduce complexity.
Alternatives to building your own edge infrastructure include leveraging managed edge services offered by major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These services offer pre-configured hardware and software, simplifying the initial setup and ongoing management.
Use Cases & Applications
The versatility of Edge Computing is evident in its diverse range of applications:
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance using sensors at the edge can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring allows for real-time analysis of vital signs, enabling faster intervention and improved patient outcomes.
- Retail: Personalized shopping experiences powered by edge analytics can optimize inventory management and enhance customer engagement.
- Smart Cities: Real-time traffic management, public safety monitoring, and environmental sensing rely heavily on edge computing for efficient operation.
- Telecommunications: 5G networks benefit greatly from edge computing to reduce latency and support new services like augmented reality and virtual reality.
Startups like FogHorn Systems and enterprises like Siemens are at the forefront of developing and deploying innovative edge-based solutions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several pitfalls can hinder successful Edge Computing adoption:
- Insufficient Security Measures: Securing distributed edge devices is crucial. Neglecting cybersecurity can expose sensitive data and create vulnerabilities.
- Overlooking Bandwidth Limitations: While reducing the need to send large datasets to the cloud is a key benefit, edge devices still need connectivity. Ensure sufficient bandwidth is available.
- Ignoring Device Management: Managing a large number of distributed edge devices can be complex. Implement robust device management tools.
- Lack of Clear Use Case Definition: Implementing edge computing for the sake of it won’t yield results. Start with well-defined use cases that address specific business needs.
Maintenance, Security & Long-Term Planning
Maintaining a robust Edge Computing infrastructure requires ongoing attention:
- Regular Software Updates: Keep firmware and software on edge devices up-to-date to address security vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Device Monitoring: Implement tools for monitoring device health and performance to proactively identify and resolve issues.
- Secure Communication Protocols: Utilize encryption and secure communication protocols to protect data in transit.
- Scalability Planning: Design your edge infrastructure with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and expanding data volumes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of and comply with relevant data privacy regulations in the regions where your edge devices are deployed.
Summary & Key Takeaways
Edge Computing is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a transformative technology reshaping industries. By bringing computation closer to the data source, it enables real-time processing, reduces latency, enhances security, and unlocks new possibilities for innovation. The market is poised for significant growth, driven by advancements in 5G, AI, and distributed architectures. While challenges exist, a strategic approach to planning, security, and device management can pave the way for successful Edge Computing implementation.
FAQs
Is it too late to invest in Edge Computing?
Absolutely not! The Edge Computing market is still in its early stages of mass adoption, presenting significant growth opportunities for investors.
How can small businesses use AI with Edge Computing?
Small businesses can leverage edge devices for local data analysis, such as optimizing inventory levels in a retail store or performing real-time quality checks in a manufacturing setting.
What tech stacks scale best for Edge Computing?
Tech stacks based on containerization (like Docker and Kubernetes) and open-source frameworks offer excellent scalability for edge deployments.
Have Thoughts?
We’d love to hear your perspective! Share your experiences with Edge Computing or any questions you might have in the comments below. Don’t forget to share this article with your network! You might also find these related articles helpful: [Link to related article 1] and [Link to related article 2].
Share this content:













Post Comment